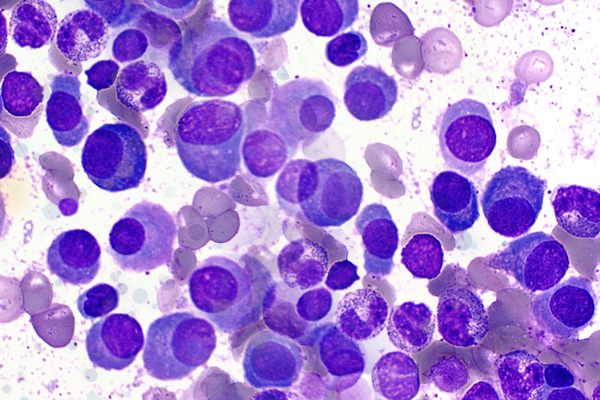
Overview
A type of white blood cell called a plasma cell makes antibodies that fight infections in your body. Plasma cell neoplasms occur when abnormal plasma cells form cancerous tumors in bone or soft tissue. These cancerous cells let too much protein (called immunoglobulin) into your bones and blood. It builds up throughout your body and damages your organs.
Not only do the cancerous plasma cells crowd out regular blood cells in your bones, they also send out chemicals that trigger other cells to eat away at your bones. The weak areas that this creates in your bones are called lytic lesions.
When there is only one tumor, the disease is called a plasmacytoma. When there are multiple tumors it is called multiple myeloma, also known as Kahler's disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of multiple myeloma vary depending on the person. Initially, symptoms may not be noticeable. However, as the disease progresses, most people will experience at least one of four major types of symptoms. These symptoms are generally referred to by the acronym CRAB, which stands for:
- Calcium
- Renal failure
- Anemia
- Bone damage
High levels of calcium in the blood come from affected bones leaking calcium. Too much calcium can cause:
- Extreme thirst
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Upset stomach
- Loss of appetite
Confusion and constipation are also common symptoms of increased calcium levels.
Kidney failure can be caused by high levels of M protein in the body.
Anemia is a condition in which the blood doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to the rest of the body. This happens when cancerous cells outnumber red blood cells in the bone marrow. Anemia often causes fatigue, dizziness, and irritability.
Bone injuries and fractures occur when cancerous cells invade the bone and bone marrow. These lesions appear as holes on X-ray images. They often cause bone pain, especially in the:
Additional symptoms of multiple myeloma may include:
- Weakness or numbness, especially in the legs
- Unintentional weight loss
- Confusion
- Problems with urination
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Repeated infections
- Vision loss or vision problems